Preface
The influence of a periodic forcing term on the Duffing equation is considered in this section.
Return to computing page for the first course APMA0330
Return to computing page for the second course APMA0340
Return to Mathematica tutorial for the first course APMA0330
Return to Mathematica tutorial for the second course APMA0340
Return to the main page for the first course APMA0330
Return to the main page for the second course APMA0340
Return to Part III of the course APMA0340
Introduction to Linear Algebra with Mathematica
Glossary
Forced Duffing equation
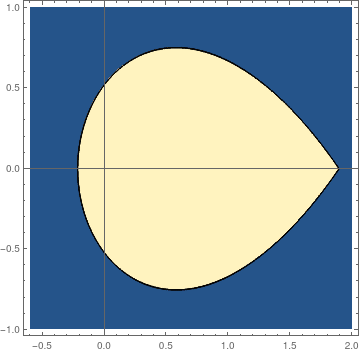
|
We plot the stability boundary for the forced Duffing equation
\[
\ddot{x} + x(t) + \frac{1}{6}\, x^3 = \frac{1}{3}\,\cos \left( \frac{3t}{5} \right) , \qquad x(0) =a, \quad \dot{x}(0) = b .
\]
pfun = ParametricNDSolveValue[
{x''[t] == -x[t] + x[t]^3/6 + (1/3)*Cos[3*t/5], x[0] == a,
x'[0] == b},
x, {t, 0, 100}, {a, b}];
fun[a_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ] := Module[ {res}, res = Quiet[pfun[a, b]]; Boole[res["Domain"] === {{0., 100.}}] ]; plot = ContourPlot[fun[a, b], {a, -0.6, 2}, {b, -1, 1}, PlotPoints -> 50, MaxRecursion -> 3, Axes -> True, AxesOrigin -> {0, 0}] |
|
| Stability boundary. | Mathematica codes. |
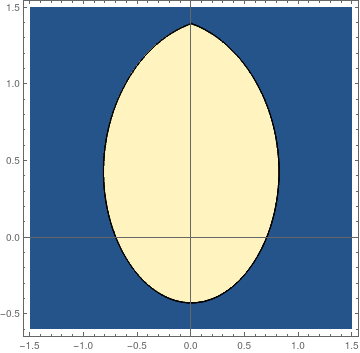
|
We plot the stability boundary for the forced Duffing equation
\[
\ddot{x} + x(t) + \frac{1}{6}\, x^3 = \frac{1}{3}\,\sin \left( \frac{3t}{5} \right) , \qquad x(0) =a, \quad \dot{x}(0) = b .
\]
pfun = ParametricNDSolveValue[
{x''[t] == -x[t] + x[t]^3/6 + (1/3)*Sin[3*t/5], x[0] == a,
x'[0] == b},
x, {t, 0, 100}, {a, b}];
fun[a_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ] := Module[ {res}, res = Quiet[pfun[a, b]]; Boole[res["Domain"] === {{0., 100.}}] ]; plot = ContourPlot[fun[a, b], {a, -1.5, 1.5}, {b, -0.6, 1.5}, PlotPoints -> 50, MaxRecursion -> 3, Axes -> True, AxesOrigin -> {0, 0}] |
|
| Stability boundary. | Mathematica codes. |
Return to Mathematica page
Return to the main page (APMA0340)
Return to the Part 1 Matrix Algebra
Return to the Part 2 Linear Systems of Ordinary Differential Equations
Return to the Part 3 Non-linear Systems of Ordinary Differential Equations
Return to the Part 4 Numerical Methods
Return to the Part 5 Fourier Series
Return to the Part 6 Partial Differential Equations
Return to the Part 7 Special Functions